Doppler Effect Wavelength Front Calculator
The Doppler effect (or Doppler shift), named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who proposed it in 1842 in Prague, is the change in frequency of a wave (or other periodic event) for an observer moving relative to its source. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren or horn approaches, passes, and recedes from an observer. Compared to the emitted frequency, the received frequency is higher during the approach, identical at the instant of passing by, and lower during the recession.
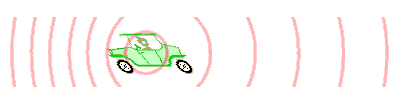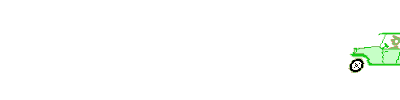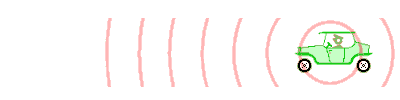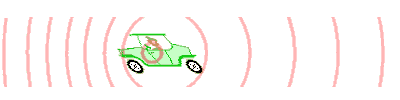
An animation illustrating how the Doppler effect causes a car engine or siren to sound higher in pitch when it is approaching than when it is receding. The pink circles are sound waves. When the car is moving to the left, each successive wave is emitted from a position further to the left than the previous wave. So for an observer in front (left) of the car, each wave takes slightly less time to reach him than the previous wave. The waves "bunch together", so the time between arrival of successive wavefronts is reduced, giving them a higher frequency. The waves "stretch apart", so the time between the arrival of successive wave-fronts is increased slightly, giving them a lower frequency.
Doppler Effect Wavelength Front:
Wavelength in Front of a Moving Source:
λf=(v-us) / f0
where,
λf = Wavelength in Front of a Moving Source
v = Wave Velocity
us = Source Velocity
f0 = Source Frequency.
